這邊就不探討怎麼建置這些CI/CD工具。
我們先採用線上有免費額度的Gitlab服務,在指定的repository上設定webhook。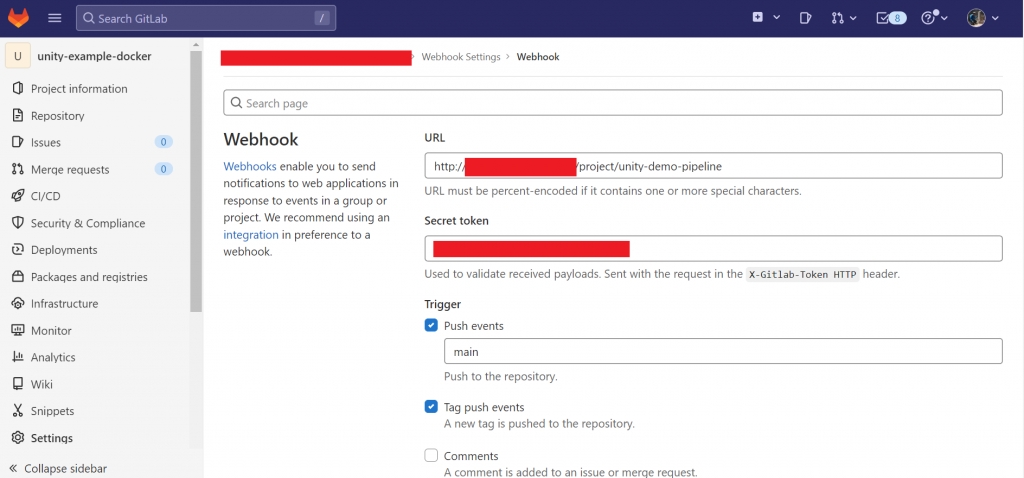
這會在每一次使用者commit code與push tag的時候,觸發Jenkins上相對的project,並執行其中寫好的pipeline程序。
Jenkins上所謂的pipeline,就是一連串循序的工作流程,在CI的建置上廣泛運用,包含執行unit test、build code、upload image、deploy等過程,是軟體開發不可缺少的一環。因此git加上pipeline-as-code已經成為軟體產品開發中,必要有的一部分。
一個簡單的pipeline script如下:
pipeline {
agent any
environment {
GITLAB_API_TOKEN = credentials('gitlab-token')
}
stages {
stage('CI Test') {
steps{
script {
sh("pip install pytest")
sh("pytest")
}
}
}
stage('Deploy Image') {
steps{
script {
docker.withRegistry("https://${registry}", registryCredential ) {
sh("docker build -t image-name:${version} .")
sh("docker tag image-name:${version} ${registry}/image-name:${version}")
dockerImage = docker.image("${registry}/image-name:${version}")
dockerImage.push()
}
}
}
}
}
}
其中Jenkins提供store credentials(read only)使用的功能,避免有人破解站台後取得密碼。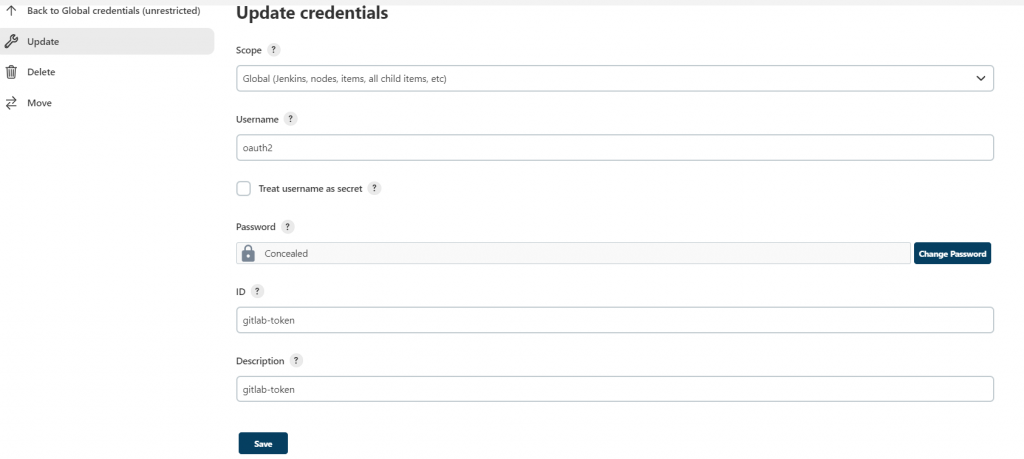
Jenkins比較麻煩的就是plugins太多,因年代久遠,有些品質參差不齊,使用時需注意查看該plugin是否已deprecated,否則反而造成設定與使用上的複雜化,就本末倒置。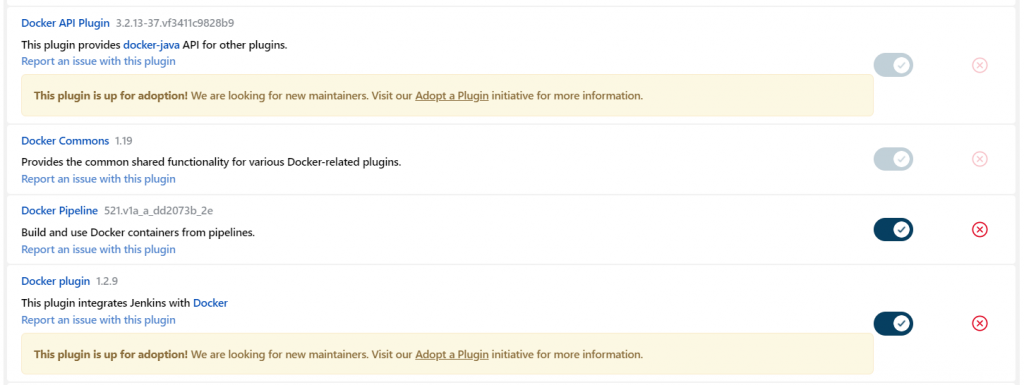
這邊列出Jenkins主要在CI上使用的plugins有:
所以簡單說,CI(Continuous integration)主要是透過每一次程式碼的commit code,來觸發程式碼品質的確認,如執行unit test與build code,確認這一次code commit是沒有問題的。
